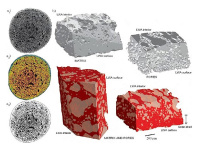
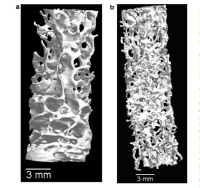
Non-destructive method for small sample studies (maximum size 5 cm lenght x 2 cm diameter). Provides a 3D microscopy, in which in a single sampling step (without the need for preparation: cutting and or fine polishing) and processing of the digitized information, a model (virtual image) of the internal spatial structure of the sample can be obtained with high resolution (micrometric scale).It also possible to recover the "intact" sample at the end of the process.
Equipment that enables highly precise and reproducible conditions for humidity, temperature and gas, testing in many different domains.
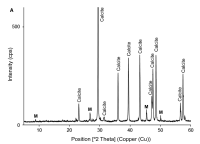
X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD) relies on the fact that different crystalline phases within a material generate distinct diffraction patterns. Identifying these phases involves comparing the X-ray diffraction patterns of unknown samples with those stored in reference databases. This technique is flexible, rapid, and non-destructive, providing comprehensive information about the crystallographic structure, chemical composition, and physical properties of a substance.
The minimal sample preparation needed is a significant factor contributing to the technique's popularity. It is well-suited for various applications, including industrial processes and materials research.
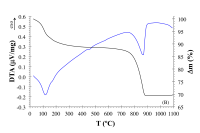
Enables simultaneous thermogravimetric and calorimetric analyses of inorganic materials from room temperature into the high temperature range of 1650°C.
For anion and cation chemical analysis in waters, rocks, sediments, soil, and plants samples after physicochemical preparation.
X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) is a fast, non-destructive, multi-element method of analysis that relies on the interaction between X-rays and a sample. It enables both semi-quantitative and quantitative assessments of material composition and may be applied to solids, liquids, and powders. This technique finds application across a diverse range of materials such as ceramics, minerals, glasses, polymers, and metals, serving various industries including metallurgy, forensics, electronics, archaeology, environmental analysis, geology, and mining.